Cough/Shortness of Breath
Table Of Contents
- Cough-Shortness of Breath
- ACE Inhibitor Use
- Airway Obstruction
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Anaphylaxis
- Anemia
- Asthma
- Exercise-Induced Asthma
- Bronchiectasis
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- COPD-chronic bronchitis
- COPD exacerbation (bronchitis)
- Lung Abscess
- Lung cancer/neoplasm
- Pleurodynia
- Pneumonia
- Atypical pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- URI-Associated Cough
Cough-Shortness of Breath
- Physical Exam:
- • VS: State (or WNL or WNL except…)
- • General: Patient is in no acute distress
- • HEENT: Examine mouth, throat, lymph nodes => Nose, mouth and pharynx WNL
- • Neck Exam: No JVD, no lympadenopathy
- • Chest Exam: Palpation, Percussion, Auscultation => Tactile fremitus normal, Clear breath sounds bilaterally/Clear breath sounds bilaterally, no rhonchi, rales, or wheezing; (Increase in tactile fremitus, and decrease in breath sounds on right side. No rhonchi, rales, or wheezing)
- • Heart Exam: Palpation, Auscultation => Apical impulse not displaced, RRR, S1, S2 wnl, No murmurs, rubs, or gallops heard
- • Abd Exam: Palpation, Auscultation
- • Extremities: Inspect => No cyanosis, or edema
- DDX:
- – Asthma (especially Exercise-Induced Asthma)
- – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) – Chronic Bronchitis
- – COPD Exacerbation
- – Pneumonia
- – Atypical pneumonia
- – Lung Neoplasm/Cancer
- – Tuberculosis (TB)
- – Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- – ACE inhibitors use
- – Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dysnea (PND)
- – Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- – HIV
- – Asthma (especially Exercise-Induced Asthma)
- Work-up:
ACE Inhibitor Use
- Presentation:
- Physical Exam:
- Treatment:
- Replace with ARBs
- valsartan (Diovan, Prexxartan)
- losartan (Cozaar)
- Replace with ARBs
Airway Obstruction
- Presentation:
- Physical Exam:
- Treatment:
- endotracheal tube
- tracheostomy or cricothyrotomy
Allergic Rhinitis
- Presentation:
- Physical Exam:
- Treatment:
- Self Care
- Avoid allergen and Nasal washing
- Medication
- Antihistamine – Loratadine
- Decongestant – Pseudoephedrine, Oxymetalozine
- Bronchodilator – Ipratropium
- Procedure – Desensitization
- Self Care
Anaphylaxis
- Presentation:
- – Physical Exam:
- Treatment:
- Supportive Care
- Tracheal intubation, Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), and IV fluids
- Oxygen
- Medication:
- Epinephrine (adrenaline) – to reduce your body’s allergic response.
- IV antihistamines and cortisone – to reduce inflammation of your air passages and improve breathing.
- Beta-agonist ( albuterol) – to relieve breathing symptoms.
- Supportive Care

Mikael Häggström / CC0
Anemia
Asthma
- Presentation:
- – shortness of breath, cough, and wheezing that worsen in cold air. several such episodes over the past 4 months.
- – Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by hyper-responsiveness, mucosal edema, and mucus production.
- – Recurrent episodes sx = cough, chest tightness, wheezing, and dyspnea
- – History: Recurrent attachs of dyspnea, cough, wheezing, Hx or FH of asthma
- – Physical: Wheezing (Expiratory high-pitched whistling sound made during breathing)
- Classifications:
- Mild intermittent asthma
- Sx ≤ 2 days/week
- Nighttime awakenings: 0
- Mild persistent asthma
- Sx > 2 days/week but not daily,
- Nighttime awakenings: 1–2x/month
- Moderate persistent asthma
- Sx Daily
- Nighttime awakenings: 3–4x/month
- Severe persistent asthma
- Sx Throughout the day
- Nighttime awakenings: > 1x/week
- Mild intermittent asthma
- DDX:
- Work-up:
- Treatment:
- Self Care – Quitting smoking
- Supportive Care – Oxygen therapy
- Medication
- SABA (albuterol)
- Low dose ICS
- Low dose ICS + LABA (salmeterol) or Medium dose ICS
- Medium dose ICS + LABA
- High dose ICS + LABA
- High dose ICS + LABA + Oral corticosteroids
Exercise-Induced Asthma
- Presentation:
- – During normal breathing via nose → warms and moistens air
- – When exercise breathe via mouth → inhale colder and drier air
- – Exercise-induced asthma, muscle bands around airways sensitive to these changes in temperature and humidity → contract → airway narrows
- – Sx begin 5 – 20 min after exercise started and stop 5 – 10 min after exercise stopped → Sx =
- – Coughing with asthma
- – Tightening of the chest
- – Wheezing
- – Unusual fatigue while exercising
- – SOB when exercising
- Treatment:
- Medication – albuterol inhaler
Bronchiectasis
- Presentation:
- – Localized, irreversible dilatation of part of bronchial tree
- – Involved bronchi are dilated, inflamed, and easily collapsible, resulting in airflow obstruction and impaired clearance of secretions
- – Associated with a wide range of disorders, usually from necrotizing bacterial infections, i,e, Staph, Klebsiella sp., or Bordetella pertussis
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute / Public domain
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- Presentation:
- – cough that is exacerbated by lying down at night and improved by propping up on three pillows. reports exertional dyspnea.
- – Heart’s function as a pump to deliver oxygen rich blood to the body is inadequate to meet the body’s needs.
- – Congestive heart failure can be caused by diseases that:
1) Weaken the heart muscle
2 Cause stiffening of the hear muscles
3) ↑ Oxygen demand by body tissue beyond heart’s capability to deliver. - – History: Dyspnea on exertion, pedal edema, orthopnea, hx of HTN, smoking, coronary disease
- – Physical: Rales in lungs, gallop heart rhythm, distended neck vein, distended liver
- DDX:
- Work-up:

Mikael Häggström / CC0
COPD-chronic bronchitis
- Presentation:
- shortness of breath as well as with a productive cough that has occurred over the past two years for at least three months each year. a heavy smoker.
- – Common preventable and treatable disease → characterized by persistent airflow, limitation that is usually progressive and associated with an enhanced chronic inflammatory response in the airways and the lung to noxious particles or gases.
- – History: Dyspnea, Cough, Weight loss, Pursed lip breathing, Chronic condition, Smoking history
- Physical Exam:
- – Rales in lungs, Gallop heart rhythm, Distended neck vein, Distended liver
- – COPD exacerbation have ↑ sputum production and cough
- DDX:
- Work-up:
COPD exacerbation (bronchitis)
- Presentation:
- DDX:
- Work-up:
Lung Abscess
Lung abscess on Chest Xray

James Heilman, MD / CC BY-SA
Lung abscess on Chest CT
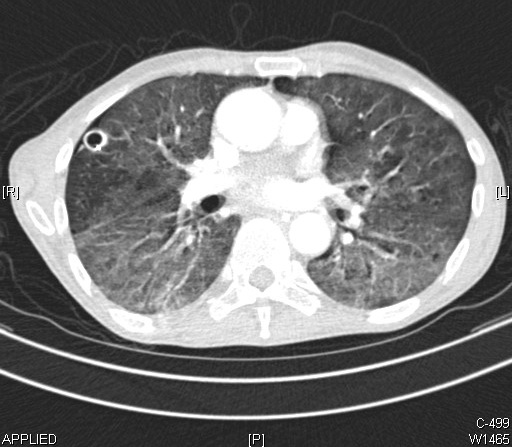
Yale Rosen from USA / CC BY-SA
Lung cancer/neoplasm
- Presentation:
- Physical exam:
- DDX:
- Work-up:
Lung Cancer on Chest Xray

James Heilman, MD / CC BY-SA
Chest CT small cell lung carcinoma

Healthengine / CC BY-SA
Pleurodynia
- Presentation:
Pneumonia
- Presentation:
- – pleuritic chest pain, fever, chills, and cough with purulent yellow sputum. a heavy smoker with COPD.
- – Classical bacterial pneumonia begins with abrupt onset of fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain and productive cough (sputum production)
- – Pleuritic pain may signal lower respiratory tract infection (diagnosis confirmed via chest exam)
- Physical Exam:
- – Fever, dullness to percussion, abnormal breath sounds, ↑ tactile fremitus
- – Signs of pulmonary consolidation on physical exam are absent 2/3s of time
- DDX:
- Work-up:
Atypical pneumonia
- Presentation:
- – two weeks of a nonproductive cough. Three weeks ago had a sore throat and a runny nose.
- – Anyone at any age can get walking pneumonia.
- – Caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Legionella species
- – M. pneumoniae is a common cause of mild pneumonia that usually affects people younger than 40
- – People who live and work in crowded places, i.e. schools, homeless shelters, prisons →↑ risk contracting it
- – Spread via resp. droplets → sx appear 15 – 25d after exposure to mycoplasma and develop slowly over 2 – 4 days
- – Symptoms include:
- – Non-Productive Cough → may come in violent spasms but produce very little mucus
- – Fever, Malaise Headache, Myalgia → Mild flu-like symptoms such as fever and chills
- – Sore throat/Hoarseness
- – Headache
- – Tiredness
- – Chest pain
- – Lingering weakness may persist after other sx gone
- – Sputum may be blood-streaked
- – GI sx prominent in Legionella infection
- – Severe ear pain d/t bullous myringitis may complicate up to 5% of Mycoplasma infections
- DDX:
- Work-up:
Tuberculosis
- Presentation:
- DDX:
- – Tuberculosis
- – Pneumonia (including Pneumocystis jiroveci)
- – Lung abscess
- – Vasculitis
- – Lymphoma
- – Metastatic cancer
- – HIV/AIDS, Acute HIV infection
- – Sarcoidosis
- Work-up:
- – CBC with diff
- – PPD
- – Sputum Grain Stain, Acid-fast stain, and Culture
- – Chest X-ray (CXR)
- – CT—chest
- – Bronchoscopy (Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL))
- – HIV antibody


