The Cardiovascular System is part of the Anatomy and Physiology section which provides High Yield information for the MCAT exam needed for Medical School.
Table Of Contents
Cardiovascular System
- A closed-circuit system composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
- Pulmonary Circuit:
- Systemic Circuit:
Pulmonary Circuit

OpenStax College / CC BY
Systemic Circuit

OpenStax College / CC BY
Arteries and Veins
| Artery | A blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to vital organs and the extremities. |
| Arterioles | Small-diameter blood vessels that extend and branch out from an artery and lead to capillaries; the primary site of vascular resistance. |
| Capillaries | The smallest blood vessels that supply blood to the tissues, and the site of all gas and nutrient exchange in the cardiovascular system. They connect the arterial and venous systems. |
| Venules | Smaller divisions of veins. |
| Veins | Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood toward the heart from vital organs and the extremities. |
Arterial Diseases
| Arteriosclerosis | A chronic disease in which thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the arterial walls result in impaired blood circulation; develops with again, and in hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and other conditions. |
Arterial and Venous System

LadyofHats / Public domain
Blood Composition
| Blood | The fluid component of the cardiovascular system that links the internal environment of the body to the external environment by transporting materials between the two environments as well as among the various cells and tissues. Therefore, its primary function is transportation. |
| Plasma | The liquid portion of the blood responsible for carrying hormones, plasma proteins, food materials (e.g., carbohydrates, amino acids, lipids), ions (e.g., sodium, chloride, bicarbonate), and gases (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide) throughout the body. |
| Platelets | One of the disc-shaped components of the blood; involved in clotting. |
| Red blood cells | Contains hemoglobin to transport oxygen |
| White blood cells | Involved in protecting against infection |
| Amount of Blood in the Body | 4.7 Litres in the average Human body |
| Four Blood Types | A, B, O, AB |
Heart Anatomy
| Heart | Serves as a pump, pushing blood throughout the body; located between the lungs and lies just left of center, behind the sternum; divided into four chambers, and is often considered two chambers in one, as the right two chambers are responsible for pulmonary circulation and the left two chambers are responsible for systemic circulation. |
| Aorta | Largest artery in the body The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body. |
| Atrium | the top two chambers of the heart |
| Ventricle | Bottom portion of the heart, thicker-walled and larger Each of the two lower chambers of the heart that pumps blood out of the heart |
| Interventricular Septum | Muscular wall that separates the right and left sides of the heart, preventing the mixing of blood from the two sides of the heart. |
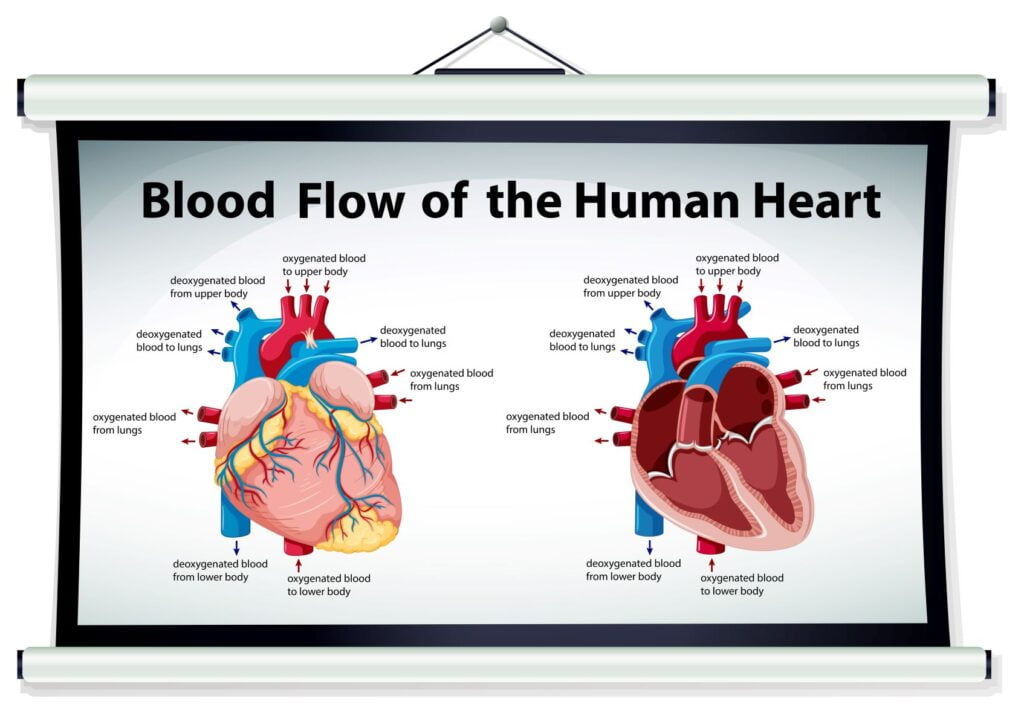
Blood Flow thru the heart
| Vena cava | Brings deoxygenated blood from systemic circulation into the right atrium |
| Right atrium | Deoxygenated blood from systemic circulation enters the heart here |
| Tricuspid valve | Between the right atrium and ventricle |
| Right ventricle | This chamber receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium and sends it out through the pulmonary artery to the lungs |
| Pulmonary valve | Valve between right ventricle and pulmonary artery |
| Pulmonary artery | This vessel carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs |
| Pulmonary vein | This vessel carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium |
| Left atrium | This chamber receives oxygenated blood from the lungs |
| Bicuspid valve | Between the left atrium and ventricle |
| Left ventricle | This chamber receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium and pumps it into the systemic circulation through the aorta |
| Aortic valve | Valve between left ventricle and aorta |
| Aorta | This vessel transports oxygenated blood from the left ventricle into the systemic circulation |

Wapcaplet / CC BY-SA
Electrical conduction of the heart
- Sinoatrial node
- Atrioventricular node
- Bundle of His
- Left bundle branch
- Left posterior fascicle
- Left-anterior fascicle
- Left ventricle
- Ventricular septum
- Right ventricle
- Right bundle branch
| Sinoatrial (SA) node | this node is known as the pacemaker of the heart. Controls the pace and rhythm of the heart beat |
| Atrioventricular (AV) node | small mass in the lower septum of the right atrium that passes impulses from the sinoatrial node toward the ventricles |
| Bundle of His | a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction that transmits the electrical impulses from the AV node (located between the atria and the ventricles) to the point of the apex of the fascicular branches via the bundle branches. |
| Atrioventricular bundle | a bundle of the modified heart muscle that transmits the cardiac impulse from the atrioventricular node to the ventricles causing them to contract |
Clinical and Physiological Values
| Heart rate | a measure of cardiac activity usually expressed as the number of beats per minute |
| Cardiac Cycle | The period from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next heartbeat; the systolic and diastolic phases and the interval in between. |
| Blood Pressure | reflects the force the blood exerts against the walls of the arteries during contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of the heart |
| Systolic pressure | the pressure generated by the left ventricle during systole |
| Diastolic pressure | blood pressure that remains between heart contractions |
| Pulse point | place where artery may be compressed against bone with fingertips to feel pulse |
| Radial pulse | the pulse located on the inside of the wrist, where the radial artery runs just beneath the skin; thumb side of arm |
| Brachial pulse | beating or throbbing felt over the brachial artery, usually palpated in the antecubital space |
| Apical pulse | A method of determining heart rate by placing the stethoscope over the apex of the heart |
Function
| Blood functions | 1. Transport 2. Protection 3. Regulation |